The rising threats of IoT devices to election, healthcare, and energy infrastructure
Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as fitness trackers and home security cameras are growing in popularity, but many people don’t realize that these devices can also be used to attack critical infrastructure. In 2017, a group of hackers used IoT devices to launch a massive attack on the internet infrastructure provider Dyn, and they were only able to do this because they were able to exploit devices that were using default passwords.
IT vs OT: Understanding the Differences
In the realm of cybersecurity, protecting both IT (Information Technology) and OT (Operational Technology) systems is essential. Comprehending the distinctions between these systems is vital for safeguarding them against cyber threats.
An Overview of the 16 Critical Infrastructure Sectors: Keeping Our Nation Secure
Critical infrastructure refers to those vital systems, networks, and assets whose incapacitation or destruction would have a debilitating effect on national security, the economy, public health, or any combination thereof. In the U.S., the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has demarcated 16 specific critical infrastructure sectors. These sectors serve as the pillars that support the nation's day-to-day operations and its citizens' way of life.
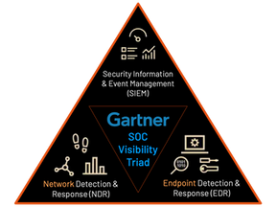
EDR and NDR
Two of the most important aspects of cybersecurity are network detection and response (NDR) and endpoint detection and response (EDR). While on the surface, there may appear to be similarities between the two, there are some key differences.
Cyberspace Solarium Commission Report
In 2019, I was honored to be asked to participate in the Cyberspace Solarium Commission (CSC), a significant initiative established in the United States as part of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019. The Commission released its report in 2020, which included a wide range of recommendations for both legislative and executive actions.
Announcing My Fellowship with Mission Critical
I am excited to announce that I have become a fellow with Mission Critical, an organization dedicated to securing the U.S.'s critical infrastructure sectors. This role complements my ongoing work at ICIT, contributing to enhancing our nation's security and resilience.